Human Herpesvirus 6 Hhv 6 Has the Following Characteristics Except
As it was the sixth herpesvirus isolated it was then subsequently renamed human herpesvirus 6. HHV-6A and HHV-6B are double-stranded DNA viruses within the Betaherpesvirinae subfamily and of.

Pdf Human Herpesvirus 6 And Malignancy A Review
Most children have been infected by age three.

. Causes Kaposis sarcoma E. Humanherpesvirus 6 HHV-6 is a recently discovered virus that onthe basis ofserologi-cal evidence seems to infect mostchildren by the age of three years However the clinical manifestations of primary HHV-6 infection and reactivation have not been well defined except for the report byYamanishi et al2 that identified HHV-6 as the agent of exanthem. Human herpes virus 6 as has human herpes virus 7 but to a lesser extent has been associated with exanthem subitum or roseola.
Appears as a mononucleosis-like illness in adults. Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 has the following characteristics except A. Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 was initially discovered in blood lymphocytes of adults with lymphoproliferative diseases or AIDS and was labeled human B-lymphotropic virus.
Then like most herpes viruses the symptoms clear and the virus enters a state of latency. Before kindergarten approximately 90 of children become infected with human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 more commonly known as sixth disease or roseola. Replicates in T lymphocytes macrophages and salivary gland tissue B.
Appears as a mononucleosis-like illness in adults. Transmitted by saliva and certain organ transplants. Causes roseola in infants and young children.
Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 has recently been identified as the agent associated with both pediatric and adult infections. Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 has the following characteristics except. A rash appears on the fourth day.
Little information is known about the clinical charac. This illness is characterized by 3 5 days of fever followed by the appearance of a maculopapular slapped cheek rash. HHV-6 species are divided into two variants.
Primary infection of HHV-6 has been associated with exanthem subitum and febrile illness. HHV-6 and HHH-7 have been associated with a variety of clinical manifestations including fever rash and seizures. A rash appears on the fourth day.
The protein encoded by the U69 open reading frame ORF of human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 has been predicted to be a protein kinase. Human herpesvirus 6 and 7 have recently been isolated. It is a very rare form of herpesvirus.
Primary infection with HHV-6B causes roseola infantum or exanthem subitum a common childhood disease that resolves spontaneously. To investigate its functional properties we have expressed the U69 ORFs from both HHV-6 variants A and B by using recombinant baculoviruses BV6AU69 and BV6BU69. Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 is a ubiquitous herpesvirus that commonly infects children younger than 3 years.
Causes roseola in infants C. It replicates in T lymphocytes macrophages and salivary gland tissue. Human herpesvirus-6 HHV-6 could reactivate under immunosuppressive conditions after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation HSCT and has the potential to.
1 Primary infection sometimes causes exanthema subitum a common exanthematic disease among infants that may be accompanied by neurologic manifestations such as febrile seizures and encephalitis. Causes roseola in infants and young children. The virion particle is 160 nm to 200 nm and has the morphologic features typical of herpes virion particles a central core containing the viral DNA a 90-nm to 110-nm capsid and a tegument layer surrounded by a membrane.
Acute HHV-6 infection is rare in immunocompetent adults but may manifest as a mononucleosislike illness characterized by fever lymphadenopathy and hepatitis. Nature Communications - Human Herpesvirus 6B HHV-6 can cause fever diarrhea and roseola rash. A prospective multicenter study was.
HHV-6 encephalomyelitis is an uncommon. After allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation HSCT human herpesvirus-6 HHV-6 can cause serious central nervous system CNS disorder and typically presents as encephalitis. Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 and human herpesvirus 7 HHV-7 are relatively recently discovered beta-herpesvirus.
Starts with a high fever. Starts with a high fever. Appears as a mononucleosis-like illness in adults D.
These closely related viruses are two of the nine known human herpesviruses herpesviruses that have humans as their primary host. Human herpes virus-6 HHV-6 infects 90100 of individuals during early childhood1 HHV-6A and HHV-6B differ in their genomes biological and immunological characteristics epidemiology and association with diseases2 Infection or reactivation is well described in the immunocompromised host population3 Reactivation occurs in up to 50 of allogeneic. Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 has the following characteristics except.
Human herpesvirus-6 HHV-6 is a major cause of limbic encephalitis with a dismal prognosis after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT HSCT. It causes roseola in infants. They are prevalent in the human population.
It is a very rare form of herpesvirus. Here the authors present a cryoEM approach to. Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 has the following characteristics except.
HHV-6 and HHV-7 belong to the Roseolovirus genus of the ß-herpesvirus subfamily. Further research identified HHV-6 in CD4 lymphocytes and as a member of the herpesviruses. The acute infection in children is characterized clinically by an acute febrile illness irritability inflammation of tympanic membranes and uncommonly a rash characteristic of roseola.
If a person who has never been infected with the varicella-zoster virus comes in contact with a person who has shingles they will come down with chicken pox Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 has the following characteristics except. Antibody prevalence for HHV-7 reaches 75 in 3- to 6-year-old children and 98 in adults 3 5. Typically it causes a 3-day fever followed by a 2-day full body rash.
Another manifestation of HHV-6 is myelitis which has not been fully evaluated. Similar to other herpesviruses HHV-6 infects a wide variety of cells and remains latent after initial infection6. Infections with human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 a ß-herpesvirus of which two variant groups A and B are recognized is very common approaching 100 in seroprevalence.
Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 is a member of the Herpesviridae family. Like other members of this family the virus remains in a latent state after primary infection has resolved and can reactivate. Human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6 is the common collective name for human betaherpesvirus 6A HHV-6A and human betaherpesvirus 6B HHV-6B.
Seroprevalence of HHV-6 reaches 80 in children 2 years 1 3.
Pdf Differential Tropism Of Human Herpesvirus 6 Hhv 6 Variants And Induction Of Latency By Hhv 6a In Oligodendrocytes

Association Of Inherited Chromosomally Integrated Human Herpesvirus 6 With Neurologic Symptoms And Management After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Transplantation And Cellular Therapy Official Publication Of The American Society For

Interaction Of Glycoprotein H Of Human Herpesvirus 6 With The Cellular Receptor Cd46 Journal Of Biological Chemistry
Human Herpesvirus 6 Infection As A Trigger Of Multiple Sclerosis An Update Of Recent Literature Bmc Neurology Full Text
Viruses Free Full Text The Spontaneous Course Of Human Herpesvirus 6 Dna Associated Myocarditis And The Effect Of Immunosuppressive Intervention Html
Pdf The Effect Of Human Herpesvirus 6 Hhv 6 On Cultured Human Neural Cells Oligodendrocytes And Microglia
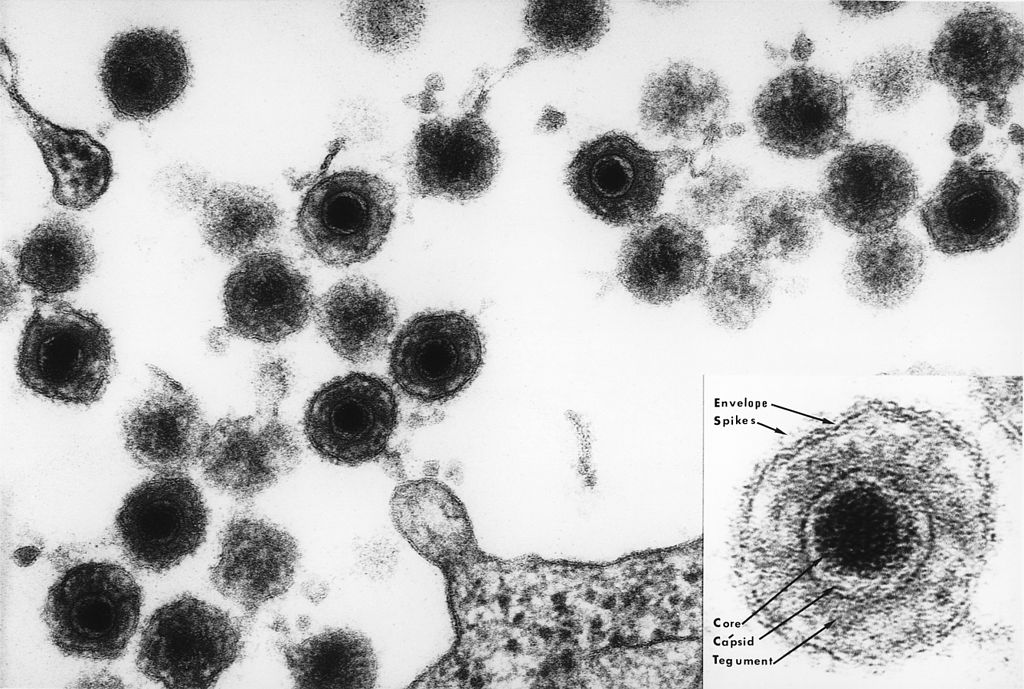
Human Herpesvirus 6 And 7 Concise Medical Knowledge

Electron Micrographs Of Mature Human Herpesvirus 6a And Human Download Scientific Diagram
Frontiers Human Herpesviruses 6a And 6b In Reproductive Diseases Immunology

Elevated Serum Cytokine Levels Are Associated With Human Herpesvirus 6 Reactivation In Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients Journal Of Infection
Human Herpesvirus 6 And 7 Concise Medical Knowledge

Herpes Simplex Virus Human Herpesvirus 6 Human Herpesvirus 8 And Download Table

Schematic Representation Of The Hhv 6 Lytic Replication Cycle The Download Scientific Diagram
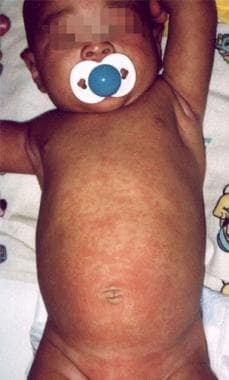
Human Herpesvirus 6 Hhv 6 Infection Clinical Presentation History Physical Examination

Pdf Identification Of Human Herpesvirus 6 Latency Associated Transcripts

Results Of Human Herpesvirus 6 Hhv 6 Antigen And Dna Determinations Download Table

References In Relationship Among Human Herpesvirus 6 Reactivation Serum Interleukin 10 Levels And Rash Graft Versus Host Disease After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Journal Of The American Academy Of Dermatology
Comments
Post a Comment